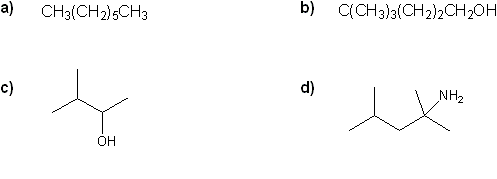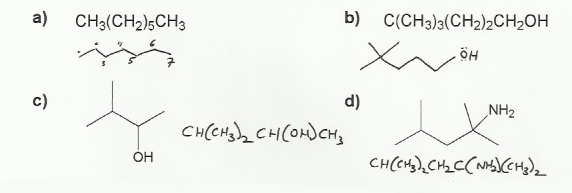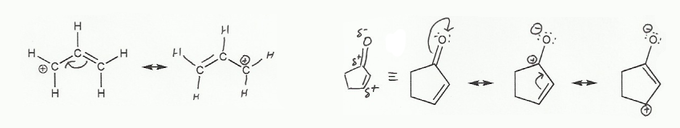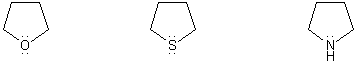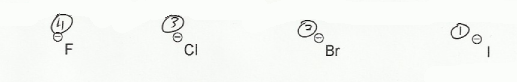Textbook: Carey and Giuliano 8th Ed. (2010)
Chapter 1: Structure Determines Properties
Practice Problems and Mendel Sets
Individual Problems
Mendel Sets
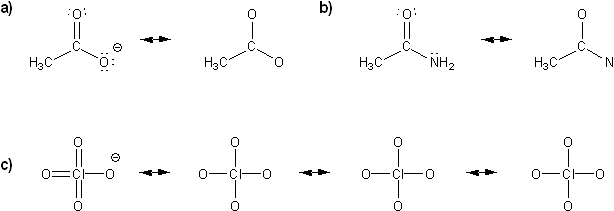
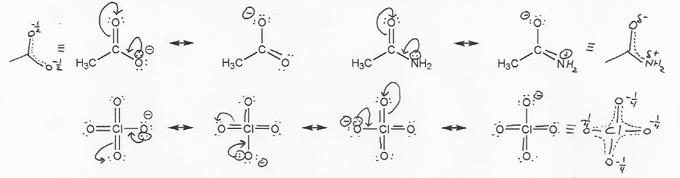
Textbook and Chapter: Carey and Giuliano 8th Ed. (2010), Chapter 1
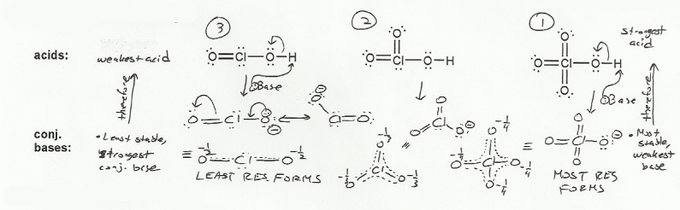
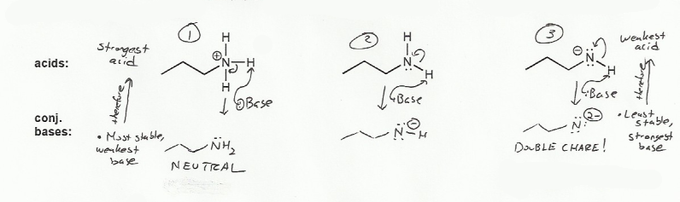
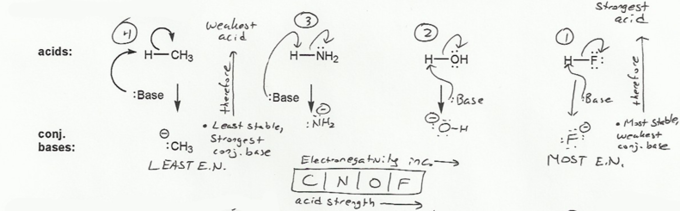
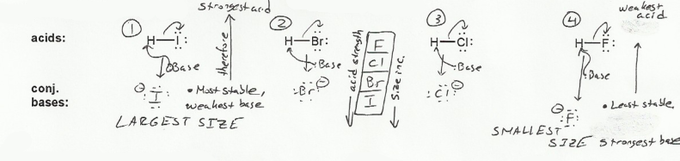
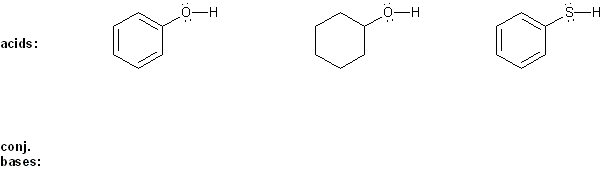
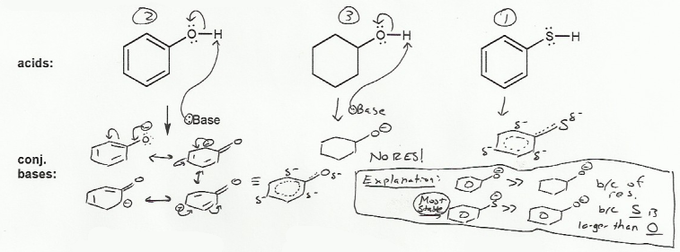
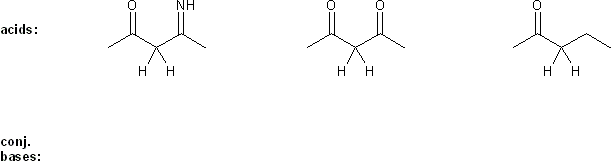
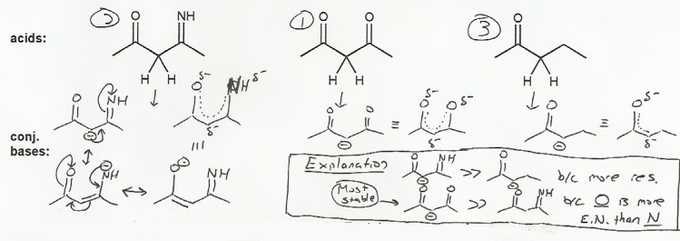
Keyword: acid strength
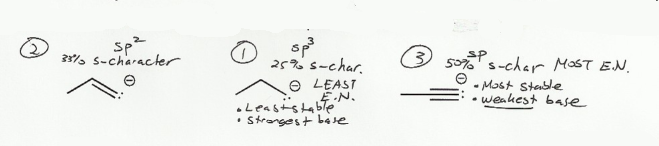
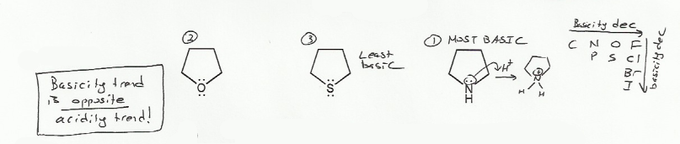
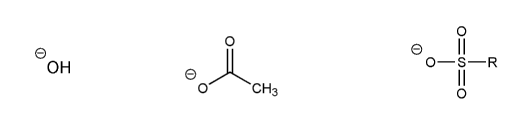
Description: This mendel set goes through rules that affect acid and base strength:
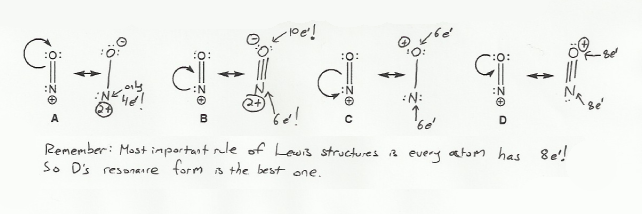
- Negative charges are best on more electronegative atoms (left to right on periodic table).
- Negative charges are best on larger atoms (up to down on periodic table).
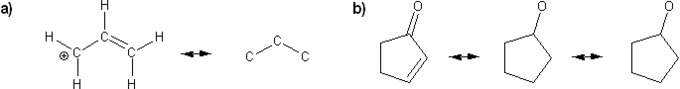
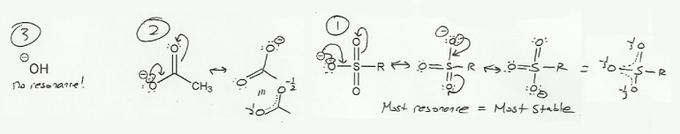
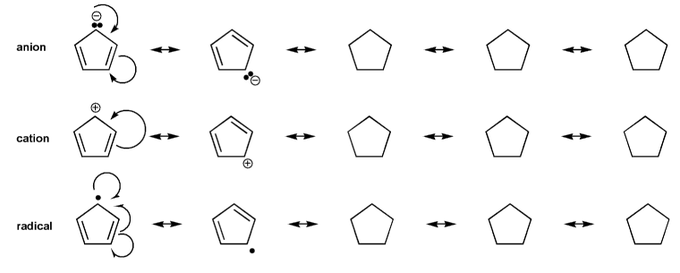
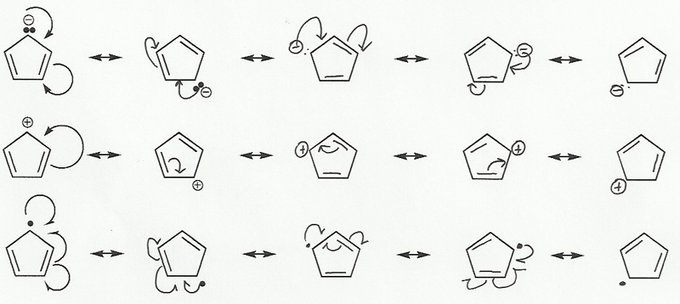
- Resonance stabilizes charges. The more resonance forms the better.
- Neutral compounds are in general more stable than changed ones.
"What makes a compound stable?" problems are key to understand for the MCAT.
Total Problems: 6
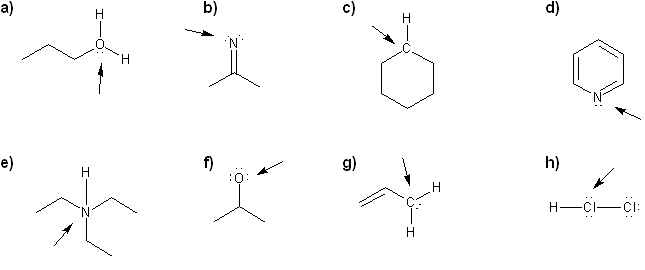
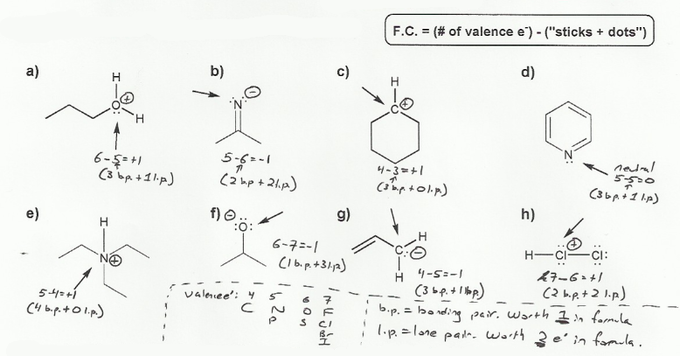
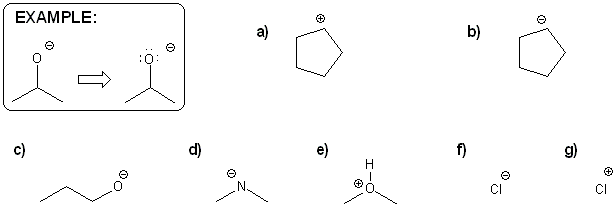
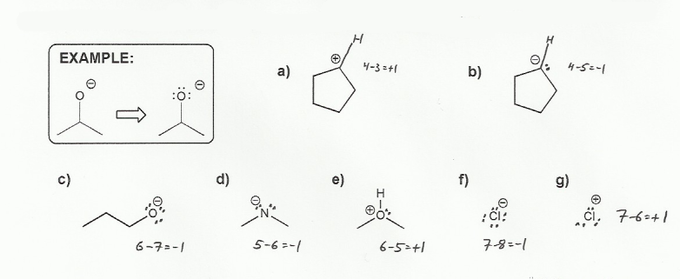
Textbook and Chapter: Carey and Giuliano 8th Ed. (2010), Chapter 1
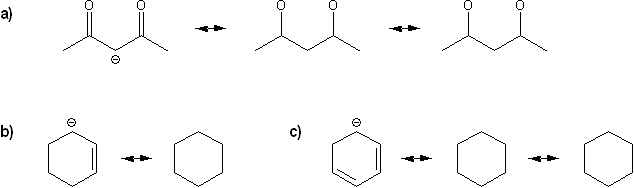
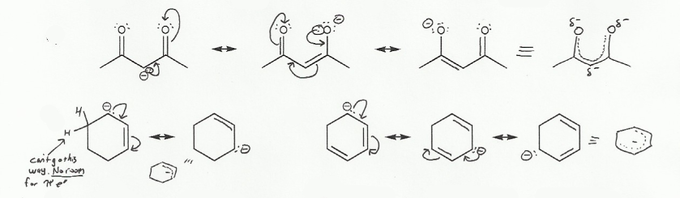
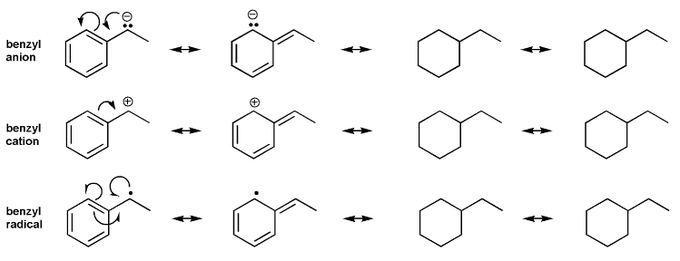
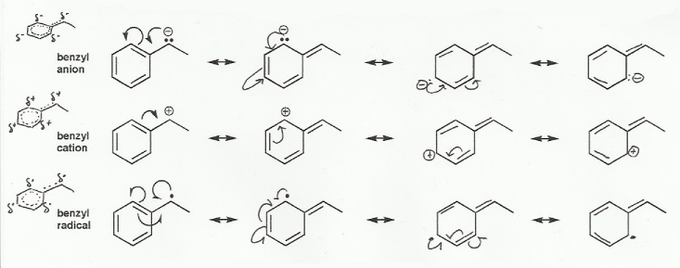
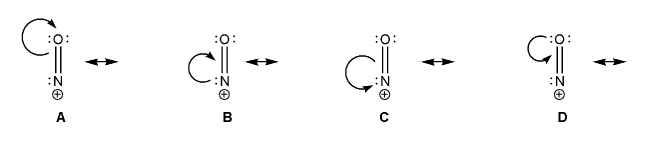
Keywords: formal charge, Lewis structures, resonance
Description: This mendel set goes through the basics of structure:
- Converting between formulas and carbon skeleton diagrams ("Zig-zag" structures)
- Determining formal charge
- Identifying implicit hydrogens and lone pairs
- Resonance and arrow pushing
Total Problems: 7