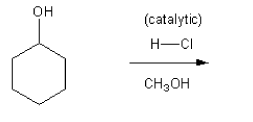
Using curved arrows, draw a mechanism for the SN1 reaction shown below.
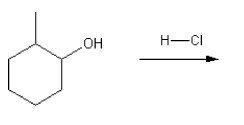
Using curved arrows, draw a mechanism for the SN1 reaction shown below.
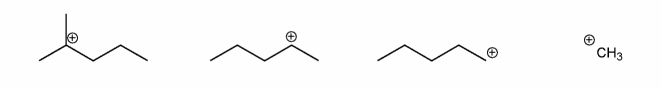
Rank the carbocations below in order of decreasing stability. (1 = most stable)
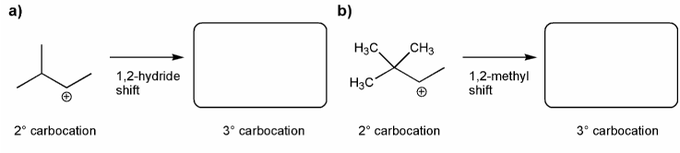
Each of the carbocations below will spontaneously rearrange. Draw the structure of the expected rearrangement product.
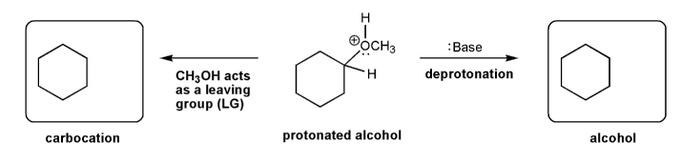
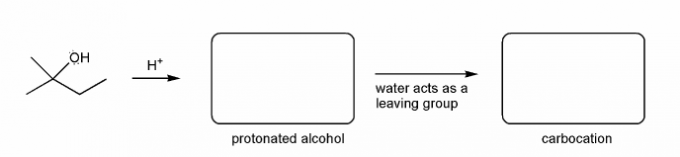
Let's go over how a carbocation can form from an alcohol.
Write in the curved arrows to show the formation of the protonated alcohol, and water acting as a leaving group to form a carbocation.
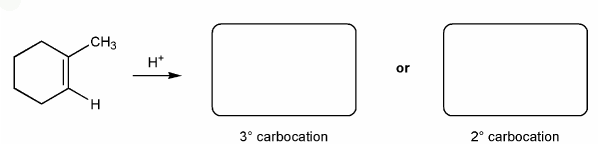
Let's go over how a carbocation can form from an alkene.
Use curved arrows to show the two carbocations that can from from 1-methylcyclohexene.
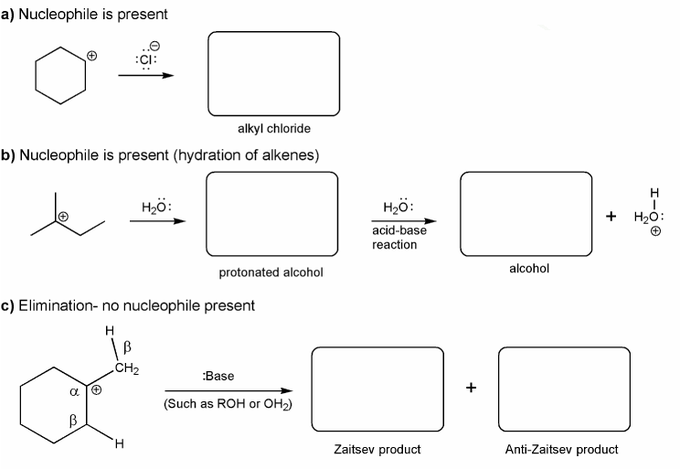
Carbocations aren't very stable and so don't last very long after they are formed.
Use curved arrows to show:
a) how a carbocation reacts with a halide ions to form an alkyl halide.
b) how a carbocation reacts with water to form an alcohol.
c) how a carbocation reacts with a base to form an alkene.
Predict the product(s) of the reaction below, and used curved arrows to show a mechanism.
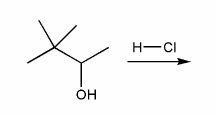
For the reaction below, draw the structures of the carbocation intermediate and the final product.
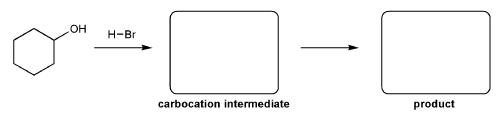
The alcohol below is protonated and contains an oxygen with a positive charge. Using curved arrows, show the two "legal moves" that result in a neutral oxygen.