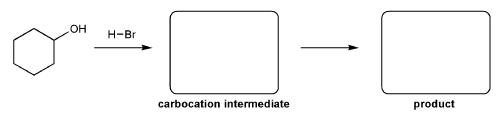
For the reaction below, draw the structures of the carbocation intermediate and the final product.
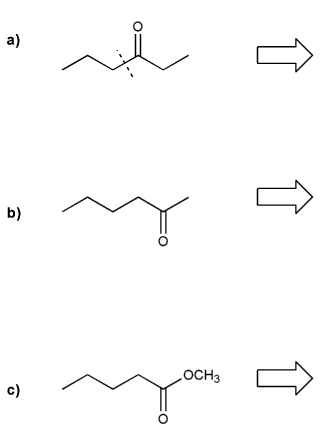
Show how each compound can be prepared from an alkene containing 3 carbons (or less).
Each answer will involve the reaction of a Grignard with either a carbonyl or epoxide.
Note: epoxides are prepared from alkenes using a peroxy acid (epoxidation) such as mCPBA.
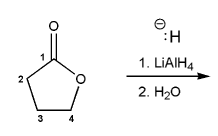
Show a mechanism for the reduction of butyrolactone using LiAlH4.
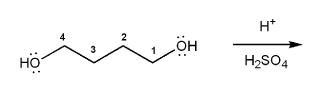
Show a mechanism for the acid-catalyzed cyclization (condensation) of 1,4-butanediol.
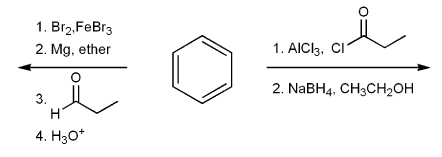
Draw the structure of the major organic product from each reaction sequence.
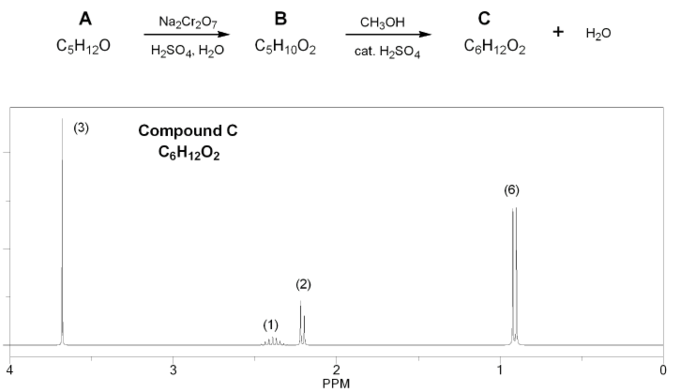
Compound A (C5H12O) is oxidized using aqueous chromium (Jones reagent) to compound B (C5H10O2), which is then treated with methanol under acidic conditions to yield compound C (C6H12O2) and water.
The 1H NMR of compound C is shown below. Determine the structures of compounds A, B, and C.
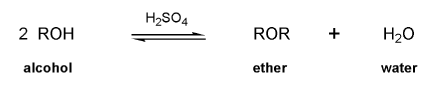
The acid-catalyzed condensation of alcohols to form ethers is reversable; ethers can be hydrolyzed back to alcohols. How can the direction of this equilibrium be controlled to preferentially form ethers?