Let's work through a 1,2 and 1,4 addition. Draw the structures for each of the species in the six boxes below. Also draw curved arrows to show electron movement.
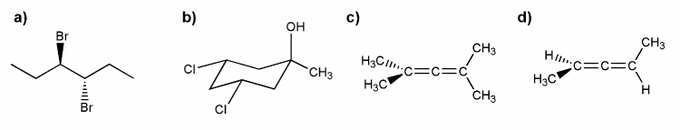
Indicate which of the molecules below are chiral (if any).
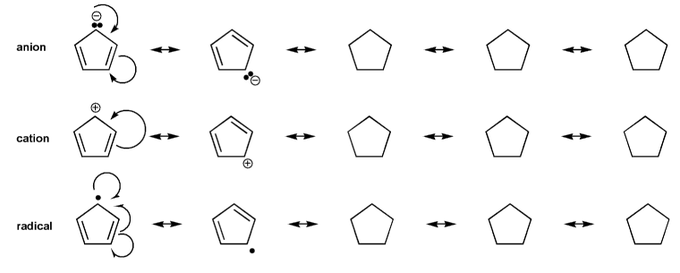
Draw all resonance forms for each species.
Rank the following dienes in order of decreasing reactivity with a dienophile in a Diels-Alder reaction. (1 = most reactive).
Write the structure of the major organic product of each reaction.
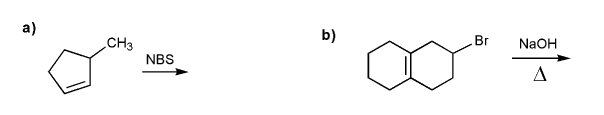
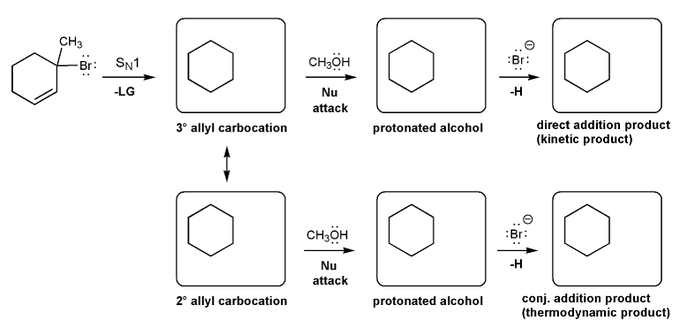
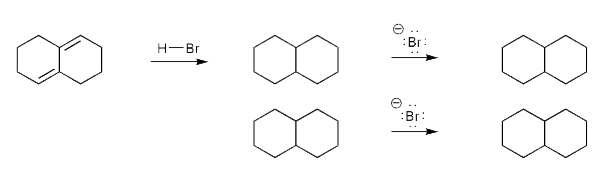
Let's work through a conjugate addition problem.
Write out the mechnanism for the formation of the 1,2 and 1,4 products of the reaction below.
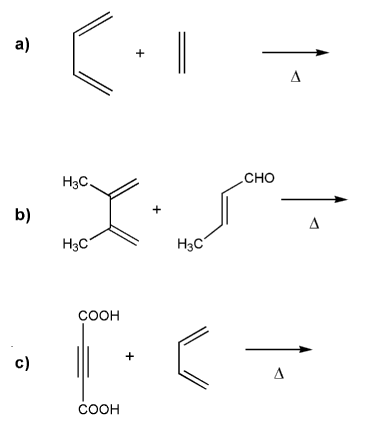
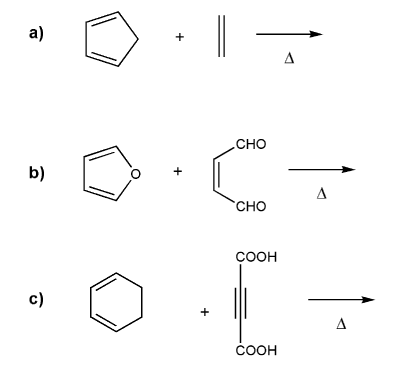
Predict the product for each Diels-Alder reaction. Indicate stereochemistry where appropriate.
Predict the product for each Diels-Alder reaction. Indicate stereochemistry where appropriate.
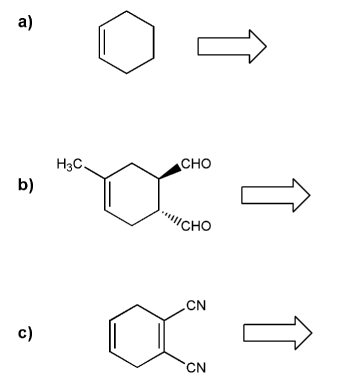
Retro Diels-Alder: show a combination of diene and dienophile that would result in each Diels-Alder adduct.
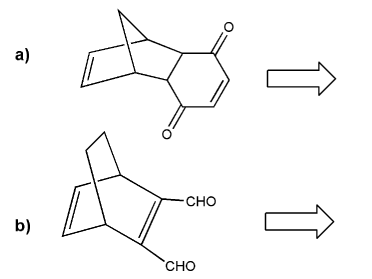
Retro Diels-Alder: show a combination of diene and dienophile that would result in each Diels-Alder adduct.
Allylic and benzylic halides tend to undergo both SN1 and SN2 substitution reactions at a faster rate than their alkyl counterparts.
For example, both allyl chloride and benzyl chloride undergo SN2 reaction at a faster rate than propyl chloride.
The same holds true for SN1 reactions: a 2° allyl or benzyl halide undergoes SN1 reaction faster than a 2° alkyl halide. Explain.