

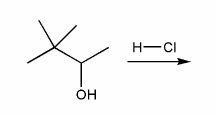
Using curved arrows, draw a mechanism for the SN1 reaction shown below.
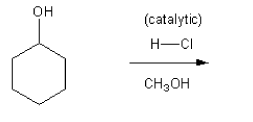
Using curved arrows, draw a mechanism for the SN1 reaction shown below.
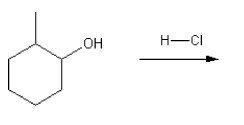
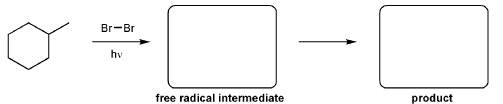
Using curved hooks, draw a mechanism for the free radical bromination reaction shown below.
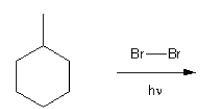
Rank the carbocations below in order of decreasing stability. (1 = most stable)
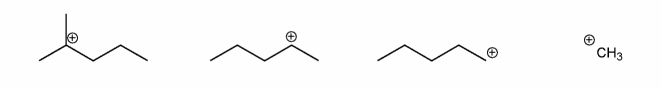
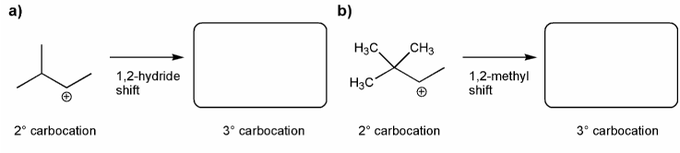
Each of the carbocations below will spontaneously rearrange. Draw the structure of the expected rearrangement product.
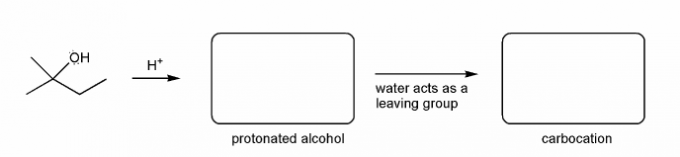
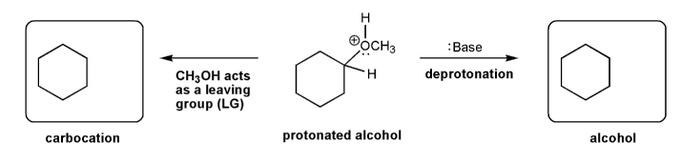
Let's go over how a carbocation can form from an alcohol.
Write in the curved arrows to show the formation of the protonated alcohol, and water acting as a leaving group to form a carbocation.
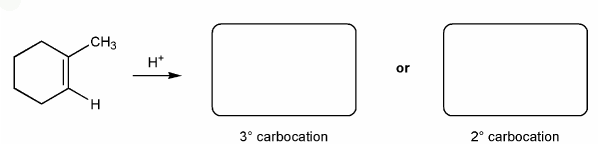
Let's go over how a carbocation can form from an alkene.
Use curved arrows to show the two carbocations that can from from 1-methylcyclohexene.
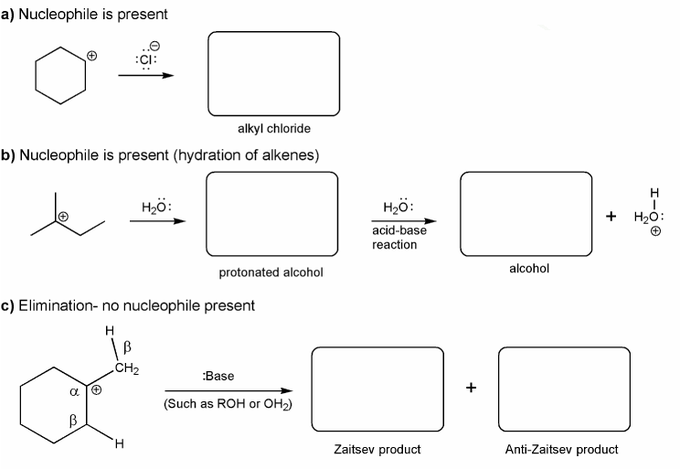
Carbocations aren't very stable and so don't last very long after they are formed.
Use curved arrows to show:
a) how a carbocation reacts with a halide ions to form an alkyl halide.
b) how a carbocation reacts with water to form an alcohol.
c) how a carbocation reacts with a base to form an alkene.
Predict the product(s) of the reaction below, and used curved arrows to show a mechanism.
For the reaction below, draw the structures of the radical intermediate and the final product.
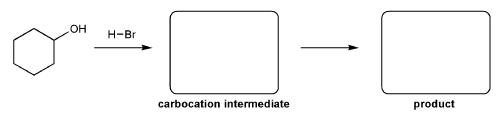
For the reaction below, draw the structures of the carbocation intermediate and the final product.
The alcohol below is protonated and contains an oxygen with a positive charge. Using curved arrows, show the two "legal moves" that result in a neutral oxygen.
Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point.
Also, make a guess about their relative solubilities in water. Explain your reasoning.
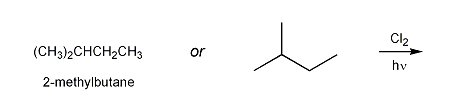
The structure of 2-methylbutane is shown below.
a) Draw the structures of all possible monochloro products resulting from the free-radical chlorination of 2-methylbutane.
b) Based on statistics alone, what do you expect the major product to be? Is this the same structure as the expected major product? Explain.
c) How would the relative yield of the products differ if bromine was used instead of chlorine?
Rank each set of compounds in order of decreasing boiling point (1 = highest boiling point):
a) ethane, n-octane, n-pentane
b) n-butane, 1-butanol, 1-chlorobutane.
c) n-octane, 2-methylheptane, 2,5-dimethylhexane
(Note that the n- prefix before an alkane just means that it's one chain, without any branching.)