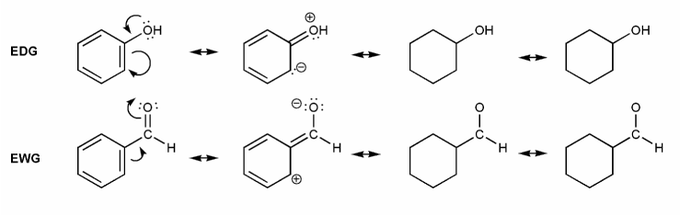
Let's draw resonance forms to see why some groups are EDG or EWG. (I've started you off)
Where are the positive or negative charges placed in EDG/EWG? (ortho/meta/para) Why would this affect EAS reactions?
Note: EDG = electron donating group, EWG = electron withdrawing group
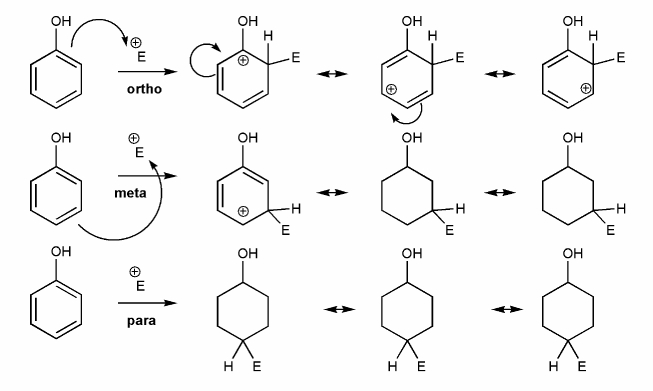
-OR is an EDG and an ortho-para director. Let's draw an EAS reaction's cyclohexadienyl cation intermediates to demonstrate why this is true. I've started you off.
What's good about ortho/para? What's bad about meta?
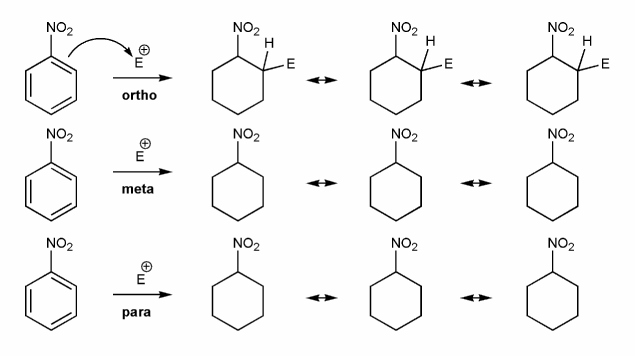
-NO2 is an EWG and a meta director. Let's draw an EAS reaction's cyclohexadienyl cation intermediates to demonstrate why this is true. I've started you off.
What's good about meta? What's bad about ortho/para?
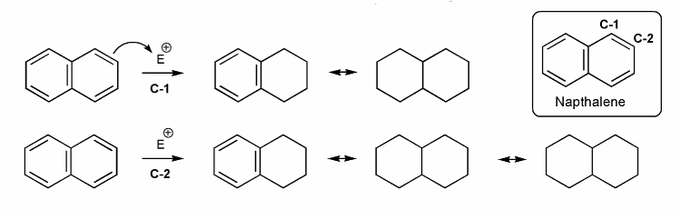
Naphthalene undergoes eletrophilic substitution at C-1.
Why is this the case, even though substitution at C-2 gives more resonance forms?