

Draw the conjugate base forms of each acid listed below, then rank the acids in order or decreasing acidity (1 = most acidic).
Explain your reasoning.
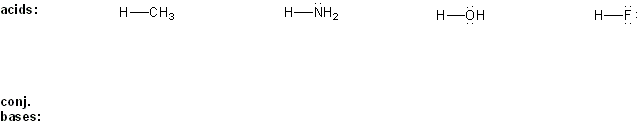
Draw the conjugate base form of each acid listed below, then rank the acids in order or decreasing acidity (1 = most acidic).
Explain your reasoning.
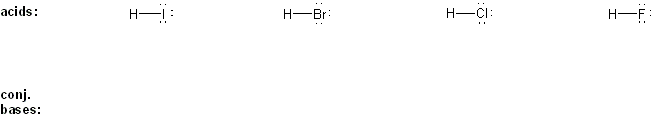
Draw the conjugate base form of each acid listed below, then rank the acids in order or decreasing acidity (1 = most acidic).
Explain your reasoning.
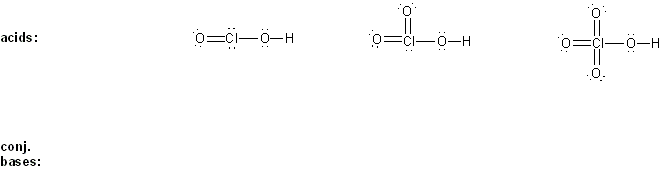
Draw the conjugate base form of each acid listed below, then rank the acids in order or decreasing acidity (1 = most acidic).
Explain your reasoning.
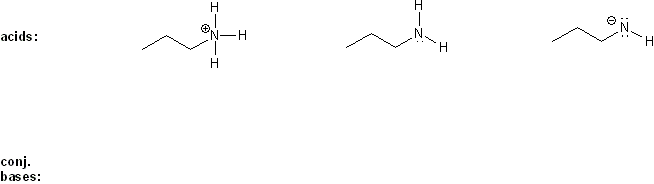
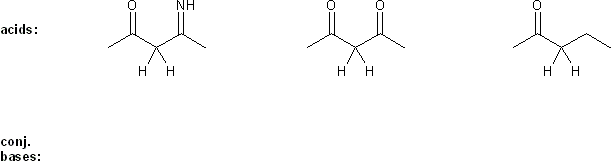
Rank each group of acids in order of decreasing acidity. (1 = most acidic)
Explain your reasoning. You will have to use more than one rule in your explanation (resonance, electronegativity, atomic radius, etc.).
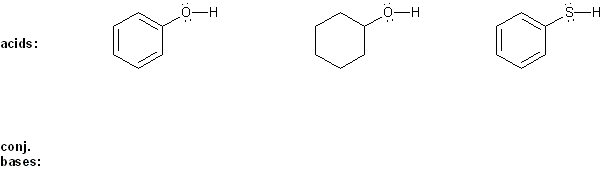
Rank each group of acids in order of decreasing acidity. (1 = most acidic)
Explain your reasoning. You will have to use more than one rule in your explanation (resonance, electronegativity, atomic radius, etc.).
Rank the group of molecules below in in order of decreasing basicity. (1 = most basic)
Explain your reasoning.
![]()
Rank the group of molecules below in in order of decreasing basicity. (1 = most basic)
Explain your reasoning.
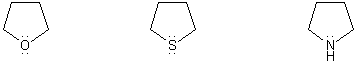
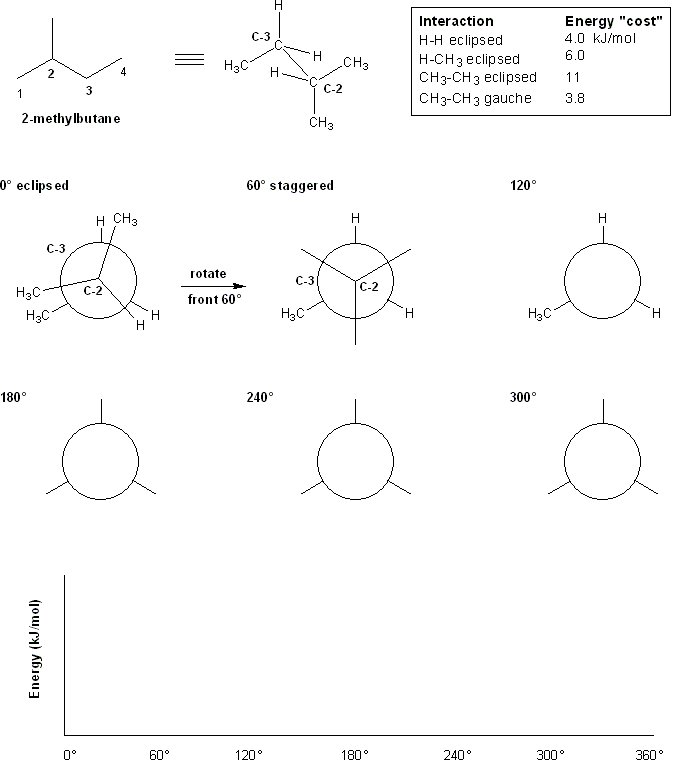
Let's perform conformational analysis on 2-methylbutane along the C2-C3 bond. We'll use the energy chart given below.
First, draw out the Newman projections along the C2-C3 bond, rotating the front carbon (C-2) by 60 degrees clockwise each time while keeping the back carbon (C-3) stationary.
According to the table above, how much energy does each conformation "cost?"
Second, make a plot of the total energy value for each Newman projection versus its dihedral angle.
Rank the following anions in order of decreasing stability (1 = most stable)
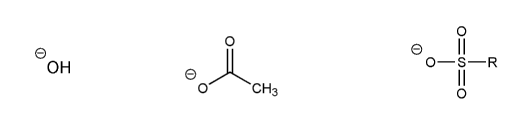
Rank the following anions in order of decreasing stability (1 = most stable)

Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point.
Also, make a guess about their relative solubilities in water. Explain your reasoning.
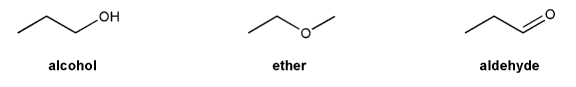
The molecule below has five different types of hydrogens (A through E). Rank each in order of decreasing acidity.
(1 = most acidic). Explain your reasoning.
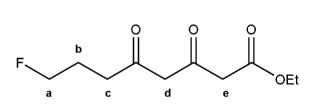
Rank each set of compounds in order of decreasing boiling point (1 = highest boiling point):
a) ethane, n-octane, n-pentane
b) n-butane, 1-butanol, 1-chlorobutane.
c) n-octane, 2-methylheptane, 2,5-dimethylhexane
(Note that the n- prefix before an alkane just means that it's one chain, without any branching.)