

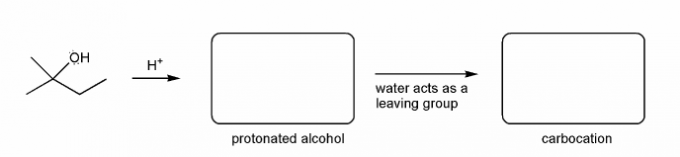
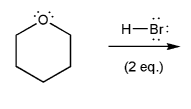
Let's go over how a carbocation can form from an alcohol.
Write in the curved arrows to show the formation of the protonated alcohol, and water acting as a leaving group to form a carbocation.
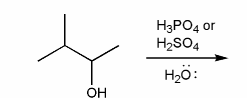
Predict the product(s) of the reaction below, and used curved arrows to show a mechanism.
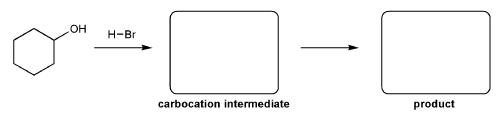
For the reaction below, draw the structures of the carbocation intermediate and the final product.
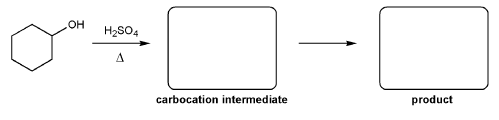
For the reaction below, draw the structures of the carbocation intermediate and the final product.
Let's work through an elimination reaction. Draw the structures for each of the species in the three boxes below (protonated thiol, carbocation, and alkene). Also draw curved arrows to show electron movement.
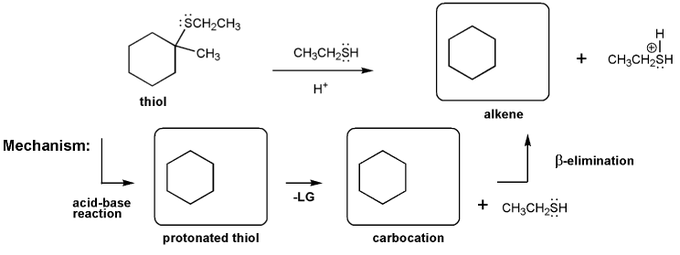
Show how each compound can be prepared from an alkene containing 3 carbons (or less).
Each answer will involve the reaction of a Grignard with either a carbonyl or epoxide.
Note: epoxides are prepared from alkenes using a peroxy acid (epoxidation) such as mCPBA.
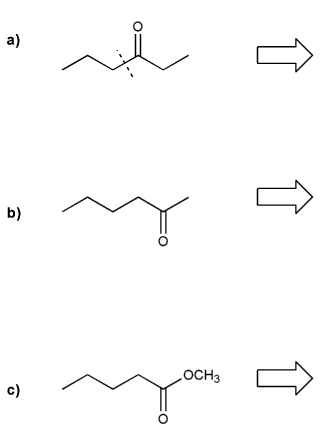
Show a mechanism for the acid-catalyzed cyclization (condensation) of 1,4-butanediol.
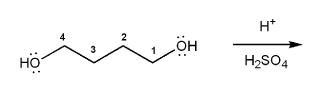
Draw the structure of the major organic product from each reaction sequence.
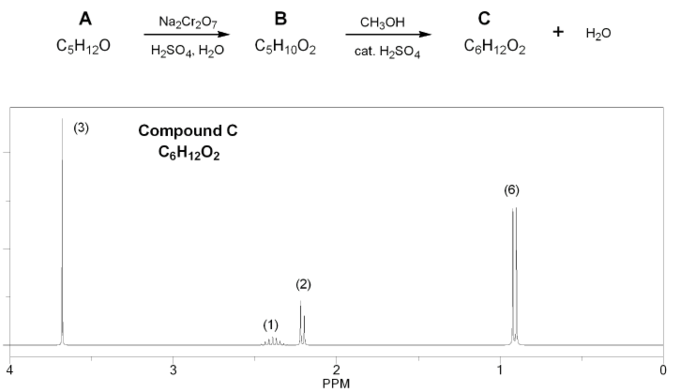
Compound A (C5H12O) is oxidized using aqueous chromium (Jones reagent) to compound B (C5H10O2), which is then treated with methanol under acidic conditions to yield compound C (C6H12O2) and water.
The 1H NMR of compound C is shown below. Determine the structures of compounds A, B, and C.
Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point.
Also, make a guess about their relative solubilities in water. Explain your reasoning.
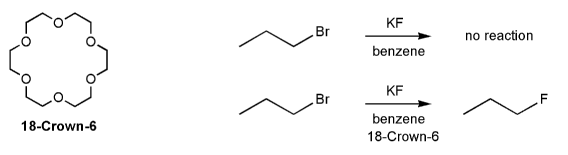
When propyl bromine is treated with KF in benzene no reaction takes place. But when the crown ether 18-Crown-6 is added to the reaction mixture the desired propyl fluoride product is produced. Explain.
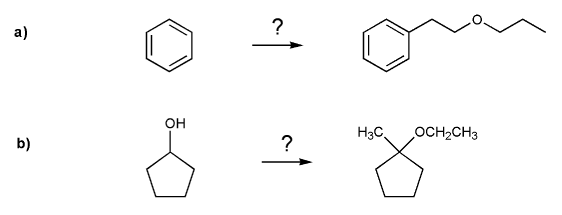
Show how each compound can be prepared from the indicated starting material.
All carbon sources must contain three carbons or less.
Write out a mechanism for the reaction below using curved arrows. Be sure to include formal charges.
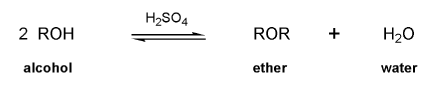
The acid-catalyzed condensation of alcohols to form ethers is reversable; ethers can be hydrolyzed back to alcohols. How can the direction of this equilibrium be controlled to preferentially form ethers?
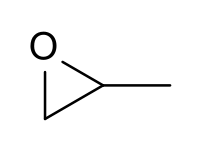
Show how to prepare each compound starting from propylene oxide.

(Propylene oxide image below courtesy of Wikipedia.)
Show two ways to prepare the ether below from a combination of an alcohol and an alkyl halide via the Williamson ether synthesis.
Is one way better than the other? Why?
