

Using curved arrows, draw a mechanism for the SN1 reaction shown below.
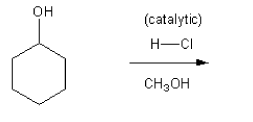
Using curved arrows, draw a mechanism for the SN1 reaction shown below.
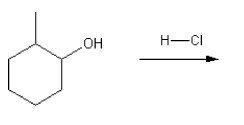
Rank the carbocations below in order of decreasing stability. (1 = most stable)
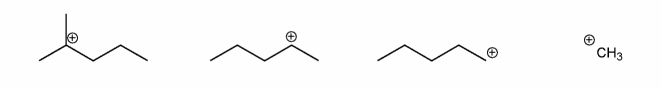
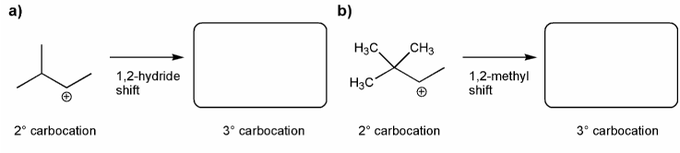
Each of the carbocations below will spontaneously rearrange. Draw the structure of the expected rearrangement product.
Let's go over how a carbocation can form from an alcohol.
Write in the curved arrows to show the formation of the protonated alcohol, and water acting as a leaving group to form a carbocation.
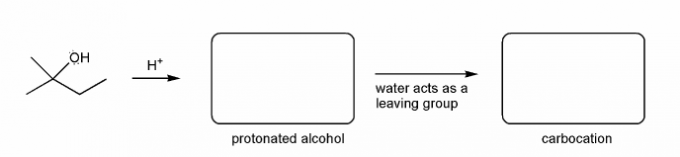
Let's go over how a carbocation can form from an alkene.
Use curved arrows to show the two carbocations that can from from 1-methylcyclohexene.
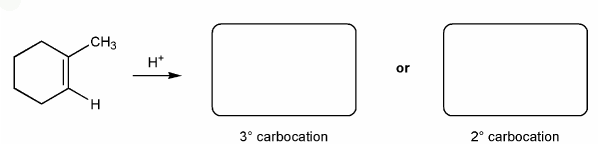
Carbocations aren't very stable and so don't last very long after they are formed.
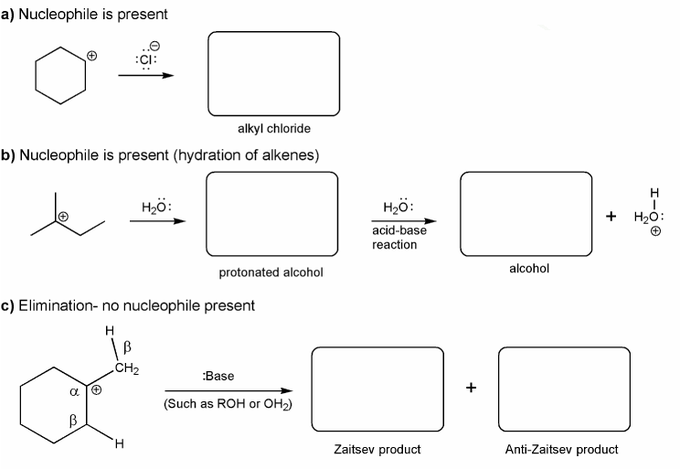
Use curved arrows to show:
a) how a carbocation reacts with a halide ions to form an alkyl halide.
b) how a carbocation reacts with water to form an alcohol.
c) how a carbocation reacts with a base to form an alkene.
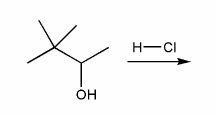
Predict the product(s) of the reaction below, and used curved arrows to show a mechanism.
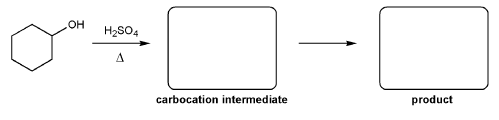
For the reaction below, draw the structures of the carbocation intermediate and the final product.
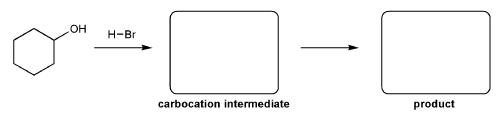
For the reaction below, draw the structures of the carbocation intermediate and the final product.
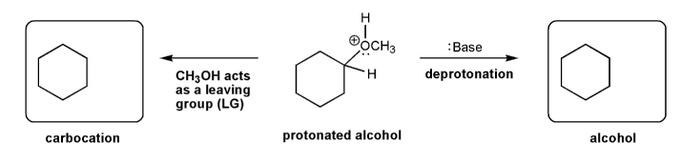
The alcohol below is protonated and contains an oxygen with a positive charge. Using curved arrows, show the two "legal moves" that result in a neutral oxygen.
Using curved arrows, draw the mechanism for the SN2 reaction below.
Rank the following anions in order of decreasing stability (1 = most stable)
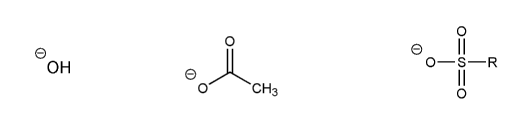
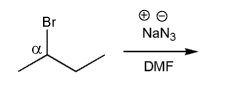
Rank the following electrophiles in order of decreasing reactivity with NaN3 in DMF. (1 = most reactive)
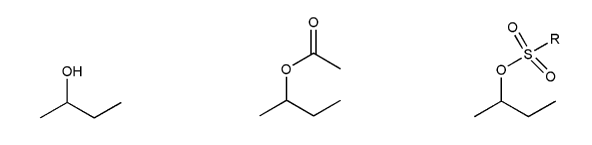
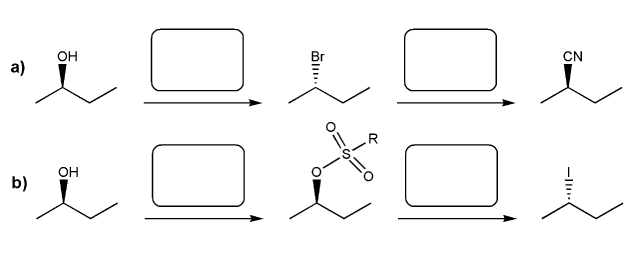
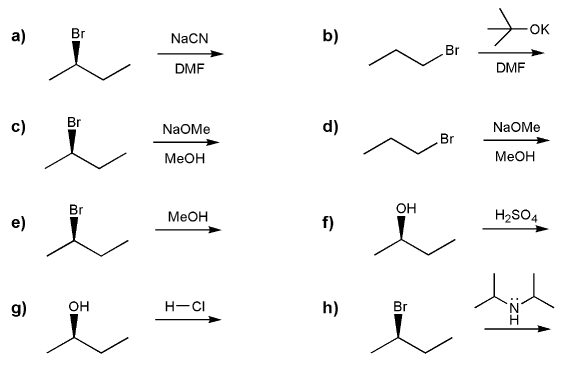
Indicate the reagents necessary to carry out each transformation.
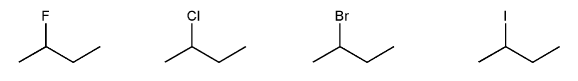
Rank the following electrophiles in order of decreasing reactivity with NaN3 in DMF. (1 = most reactive)
Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing nucleophilicity. (1 = most nucleophilic)
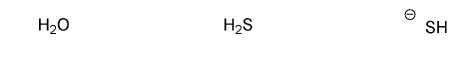
Rank the following anions in order of decreasing stability (1 = most stable)

Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing reactivity with NaI in acetone. (1 = most reactive)
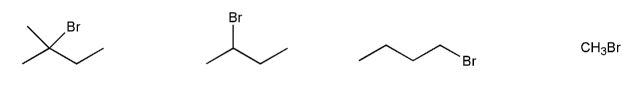
Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing reactivity with water (solvolysis). (1 = most reactive)
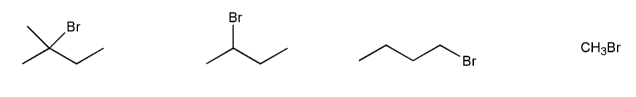
For each reaction below, determine whether the primary reaction is SN1, SN2, E1, or E2, and then draw the product.
Note: Me = methyl (CH3)
Show two ways to prepare the ether below from a combination of an alcohol and an alkyl halide via the Williamson ether synthesis.
Is one way better than the other? Why?
