Draw the conjugate base forms of each acid listed below, then rank the acids in order or decreasing acidity (1 = most acidic).
Explain your reasoning.
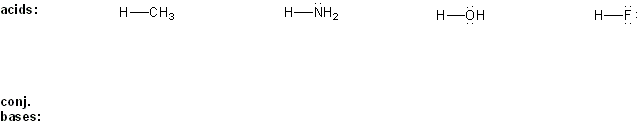
Draw the conjugate base form of each acid listed below, then rank the acids in order or decreasing acidity (1 = most acidic).
Explain your reasoning.
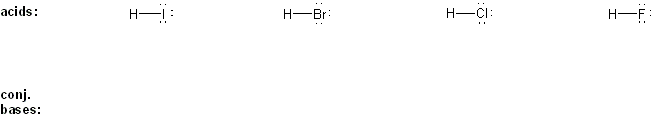
Draw the conjugate base form of each acid listed below, then rank the acids in order or decreasing acidity (1 = most acidic).
Explain your reasoning.
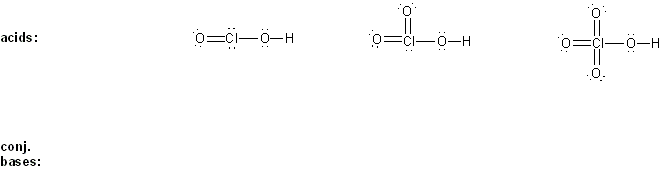
Draw the conjugate base form of each acid listed below, then rank the acids in order or decreasing acidity (1 = most acidic).
Explain your reasoning.
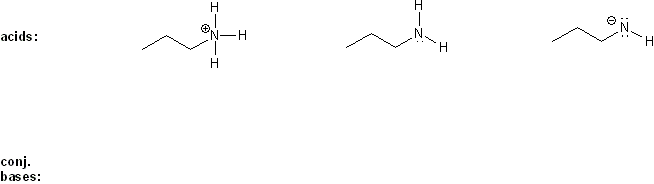
Rank each group of acids in order of decreasing acidity. (1 = most acidic)
Explain your reasoning. You will have to use more than one rule in your explanation (resonance, electronegativity, atomic radius, etc.).
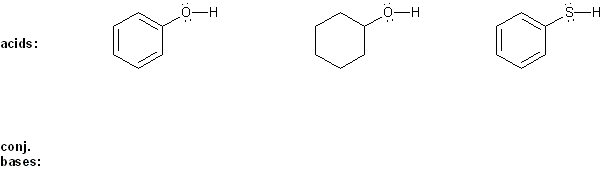
Rank each group of acids in order of decreasing acidity. (1 = most acidic)
Explain your reasoning. You will have to use more than one rule in your explanation (resonance, electronegativity, atomic radius, etc.).
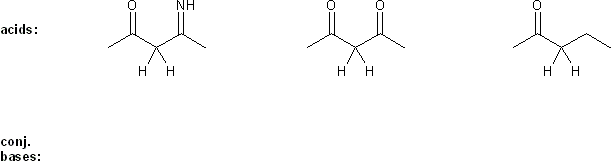
Rank the group of molecules below in in order of decreasing basicity. (1 = most basic)
Explain your reasoning.
![]()
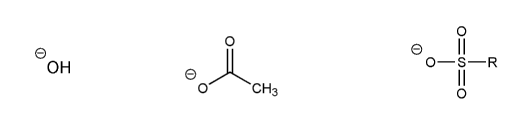
Rank the group of molecules below in in order of decreasing basicity. (1 = most basic)
Explain your reasoning.
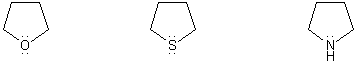
Convert each formula to a carbon skeleton diagram, or vice-versa.
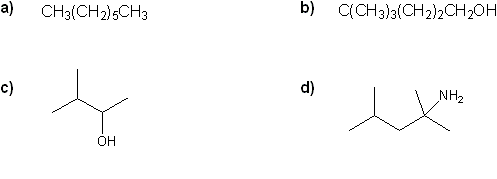
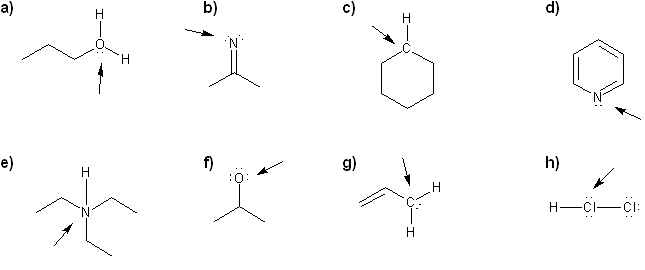
For each molecule, determine the formal charge of the indicated atom.
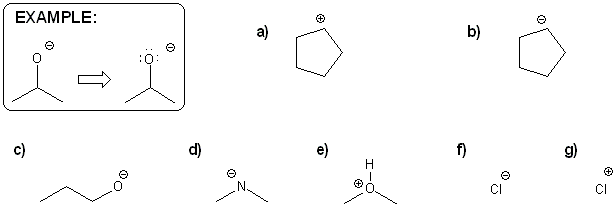
For each molecule below, draw in all implied lone pairs and/or protons (hydrogens) based on the formal charge shown.
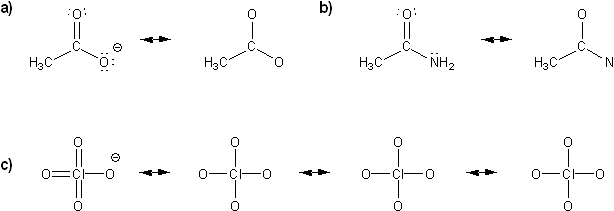
Draw all possible resonance forms for each structure below. Use curved arrows.
Note that some structures only show charge, and not implied protons or lone pairs!
Draw all possible resonance forms for each structure below. Use curved arrows.
Note that some structures only show charge, and not implied protons or lone pairs!
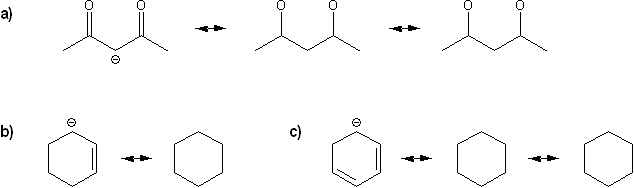
Draw all possible resonance forms for each structure below. Use curved arrows.
Note that some structures only show charge, and not implied protons or lone pairs!
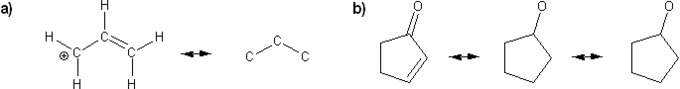
Draw all possible resonance forms for each structure below. Use curved arrows.
Note that some structures only show charge, and not implied protons or lone pairs!
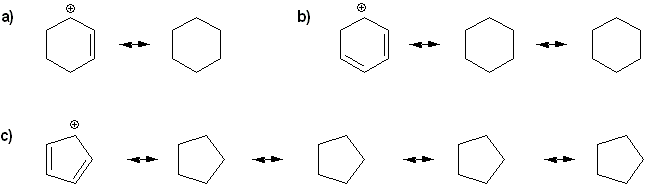
Rank the following anions in order of decreasing stability (1 = most stable)
Rank the following anions in order of decreasing stability (1 = most stable)

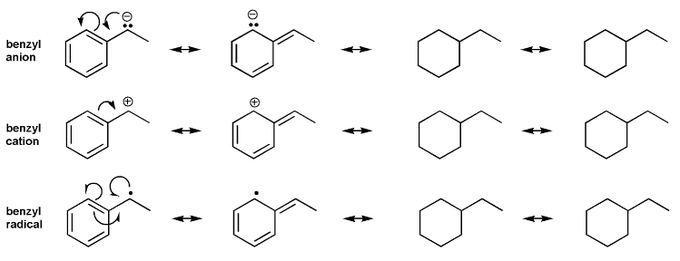
Draw all resonance forms for each species.
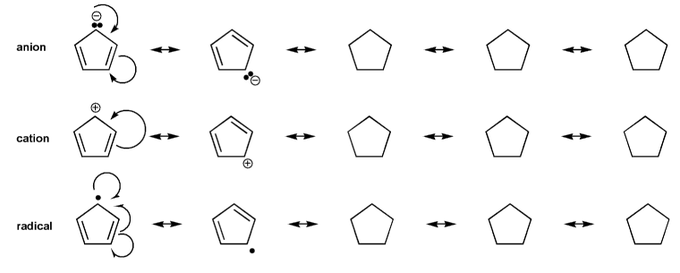
Draw all resonance forms for each species.
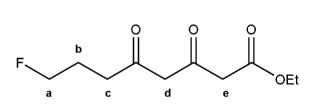
The molecule below has five different types of hydrogens (A through E). Rank each in order of decreasing acidity.
(1 = most acidic). Explain your reasoning.
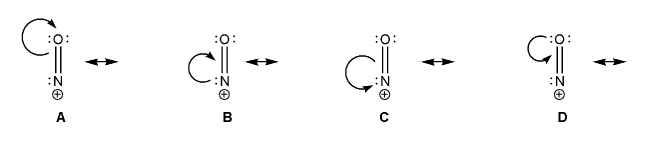
The nitrosyl cation is shown below. Also shown are several proposed resonance arrows, only one of which is correct.
Draw the resonance forms that would follow from each set of arrows, and include formal charges. Which one is the correct resonance form? Explain your reasoning.